1. Continuous, Real-World Data Collection
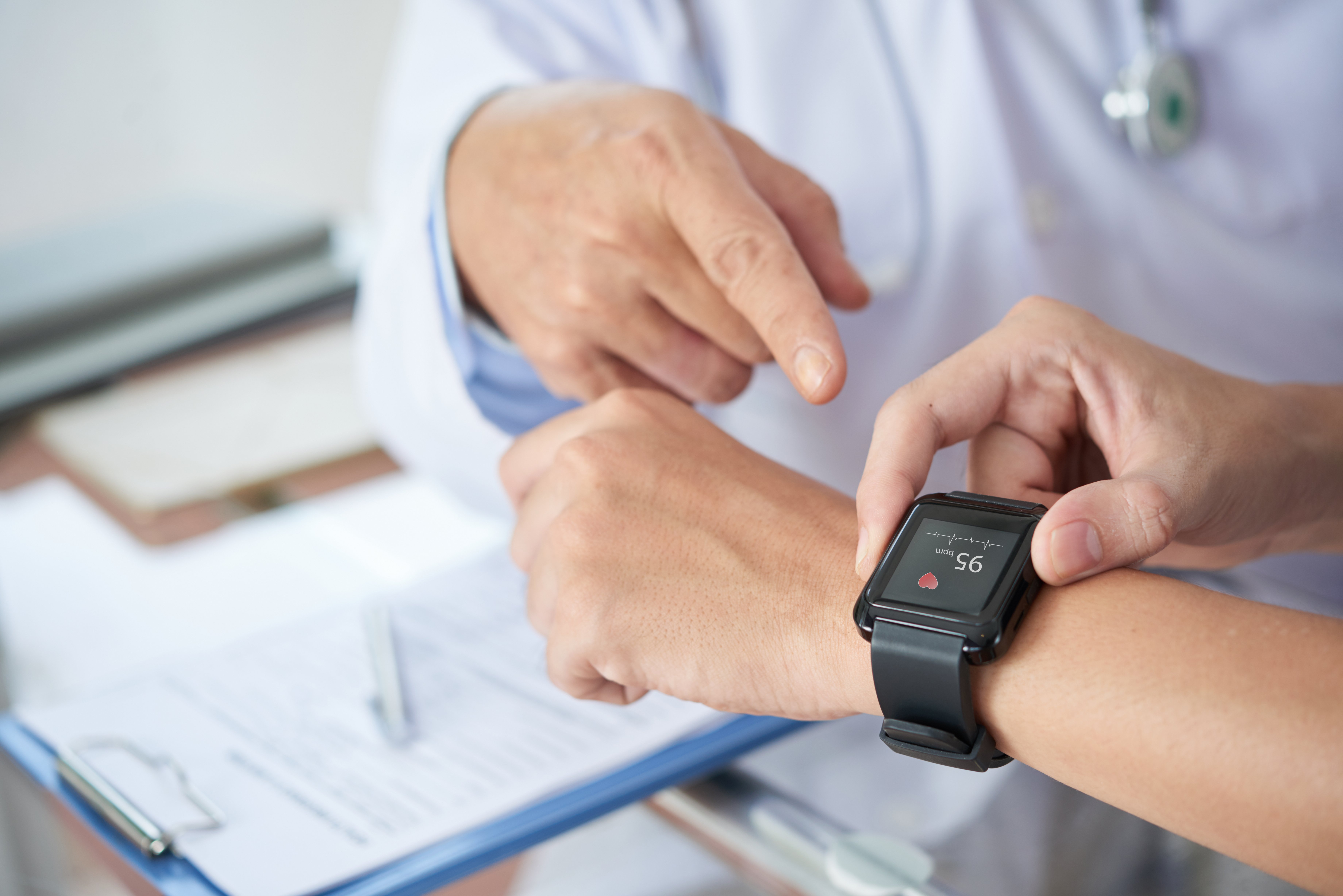


Traditional clinical trials rely heavily on in-clinic measurements taken at scheduled visits. Wearables change that paradigm by enabling:
- Continuous heart rate monitoring
- Activity tracking
- Sleep measurement
- Blood glucose monitoring (CGM)
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Oxygen saturation tracking
This allows researchers to capture real-world, longitudinal data rather than isolated snapshots.
For therapeutic areas like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, neurology, and oncology, this continuous monitoring enhances endpoint sensitivity and supports digital biomarker development.
2. Improved Patient Adherence and Engagement
One of the biggest challenges in clinical trials is patient compliance.
Missed ePRO entries.
Uncharged devices.
Incomplete diary submissions.
Gaps between visits.
Wearables reduce reliance on manual input by passively collecting data in the background. When combined with structured reminders and human oversight, adherence improves significantly.
Studies consistently show that decentralized and hybrid trials benefit from digital tools that reduce participant burden.
However, technology alone does not solve compliance.
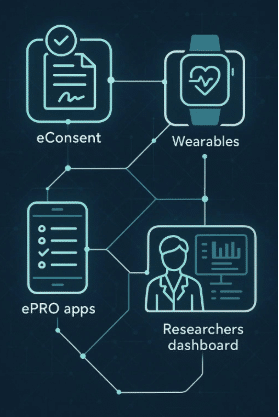
The most successful implementations pair wearables with:
- eCOA / ePRO platforms
- Automated engagement workflows
- Real-time monitoring dashboards
- Human concierge support to intervene early
When compliance gaps are identified and addressed proactively, sponsors protect endpoint integrity and reduce protocol deviations.
3. Reduced Site Burden


Sites are overwhelmed.
Expanding vendor stacks, complex protocols, and increasing regulatory demands have made execution more difficult than ever.
Wearable devices can reduce site burden by:
- Minimizing in-clinic visits
- Automating data capture
- Reducing manual data entry
- Providing centralized dashboards for oversight
When wearable data integrates directly with eCOA and study platforms, sites spend less time chasing data and more time supporting patients.
For sponsors, this translates to:
- Faster site activation
- Improved site satisfaction
- Reduced administrative overhead
4. Enhanced Data Quality and Endpoint Accuracy
Wearables improve data density, but the true advantage lies in:
- Objective measurements
- Reduced recall bias
- Higher-frequency data points
- Timestamped, validated inputs
For example:
- Continuous glucose monitors provide dynamic glucose variability data
- Activity trackers quantify functional status in oncology or rare disease trials
- Sleep tracking can correlate symptom burden in CNS studies
When validated properly, wearable-derived endpoints can support regulatory submissions and post-market evidence strategies.
However, sponsors must ensure:
- Device validation
- Data normalization
- Standardization across patient populations
- Regulatory compliance (21 CFR Part 11, ISO 27001, etc.)
Data volume without structure creates noise. Structured integration creates insight.
5. Support for Hybrid and Decentralized Trials

Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) and hybrid models depend on remote data capture.
Wearables enable:
- Fewer on-site visits
- Broader geographic recruitment
- Participation from mobility-limited populations
- Real-world evidence collection
For post-market studies, wearable devices are particularly powerful. They allow sponsors to:
- Monitor long-term outcomes
- Track safety signals remotely
- Collect adherence data post-approval
- Reduce operational costs
In a competitive regulatory environment, post-market data can be a strategic differentiator.
6. Vendor Consolidation and Operational Efficiency
A major challenge in modern clinical research is vendor fragmentation.
Sponsors often manage:
- eCOA vendor
- Wearable vendor
- Data integration vendor
- Engagement platform
- Call center
- Analytics partner
Each interface increases risk.
Integrated wearable ecosystems reduce complexity by consolidating:
- Device provisioning
- Data ingestion
- Compliance monitoring
- Patient engagement
- Site support
When wearable data flows into a unified study platform, sponsors gain visibility into adherence, device uptime, and protocol compliance in real time.
This improves execution — not just technology adoption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wearables in Clinical Trials
Are wearable devices validated for regulatory use?
Yes — many devices are validated for specific endpoints. However, sponsors must ensure appropriate validation studies, documentation, and alignment with regulatory guidance.
Do wearables replace site visits?
Not entirely. Most studies adopt a hybrid model, combining in-clinic assessments with remote monitoring.
Do wearables improve retention?
When paired with structured engagement and proactive monitoring, wearable programs can reduce dropout by identifying issues early and supporting patients between visits.
The Strategic Advantage
The adoption of wearable devices in clinical trials is no longer about innovation for its own sake.
It is about:
Protecting data integrity
Increasing patient retention
Reducing site burden
Simplifying vendor ecosystems
Improving operational execution
Sponsors who treat wearables as isolated technology often struggle.
Sponsors who integrate wearables into a cohesive workflow — combining eCOA, device management, compliance monitoring, and human oversight — achieve measurable improvements in study continuity.
Conclusion
Wearable devices are reshaping how clinical trials are conducted across therapeutic areas.
They enable continuous data collection, enhance adherence, support decentralized models, and improve endpoint sensitivity.
But the real benefit lies in disciplined execution — ensuring that wearable data is complete, validated, and actionable.
As clinical research grows more complex, wearable integration is not just a digital upgrade.
It is an operational strategy.
How do wearable devices benefit clinical trials?
They provide real-time health data, reduce manual reporting, and enhance patient engagement and compliance.
Are wearable devices secure for patient data?
Yes. Most devices follow strict data protection protocols with encryption and secure cloud storage.
Can wearables replace traditional clinical visits?
Not entirely, but they significantly reduce the need for frequent visits by allowing remote monitoring.
What kind of data do wearables collect in trials?
They collect physiological data such as heart rate, movement, sleep, temperature, and other relevant health metrics.
How do wearable devices improve participant retention?
By making participation convenient and interactive, they reduce burden and keep patients more engaged throughout the study.